Newsletter

Ypsilanti Animal Clinic Newsletter
Welcome to the Ypsilanti Animal Clinic Newsletter! We’re excited to provide you with this engaging, informative online resource crafted to keep you updated and connected to our veterinary community. Our veterinarian in Ypsilanti and dedicated team are passionate about educating pet owners and supporting them in giving their pets the best possible care. Through this newsletter, we bring you a variety of articles focused on pet health, wellness tips, and seasonal care advice, helping you stay informed on the essential aspects of your pet’s well-being.
In addition to general pet care tips, each edition of our newsletter offers updates on our clinic, from introducing new team members and sharing exciting hospital developments to highlighting specialized services we provide. Our veterinarian in Ypsilanti team is committed to staying at the forefront of veterinary medicine, which is why we also include news on the latest advancements and trends, giving you insight into modern approaches and discoveries in pet healthcare.
We want this newsletter to serve as a reliable source of knowledge and a reflection of our commitment to high-quality, compassionate care. Our veterinarian in Ypsilanti is here to support you in keeping your pet happy and healthy throughout every stage of life. Thank you for subscribing, and we hope you enjoy each informative issue of the Ypsilanti Animal Clinic Newsletter. Let us be your trusted guide in providing exceptional care for your beloved pets!
Current Newsletter Topics
Veterinarians take many things into consideration before recommending humane euthanasia for a sick, injured or elderly pet. When it comes to setting your own mind at ease, there are ways to rate or measure your pet's overall well-being.
The Veterinary Medical Center at Ohio State University published a survey designed to illustrate your pet's quality of life which was adapted from several other common methods. The survey asks you, the pet owner, to rate 25 different prompts on a scale from one to five. A score of one indicates strong agreement or a condition that is present all the time or is severe; a score of five indicates strong disagreement or a condition that is never present and nonexistent. Thus, higher scores indicate a better quality of life.

The Survey
Scale
1: Strongly Agree / All the Time / Severe
2: Agree / Most of the Time / Significant
3: Neutral / Sometimes / Mild
4: Disagree / Occasionally / Slight
5: Strongly Disagree / Never / None
My pet...
1. Does not want to play
2. Does not respond to my presence or doesn't interact with me in the same way as before
3. Does not enjoy the same activities as before
4. Is hiding
5. Demeanor/behavior is not the same as it was prior to diagnosis/illness
6. Does not seem to enjoy life
7. Has more bad days than good days
8. Is sleeping more than usual
9. Seems dull and depressed
10. Seems to be or is experiencing pain
11. Is panting (even while resting)
12. Is trembling or shaking
13. Is vomiting and/or seems nauseous
14. Is not eating well (may only be eating treats or if fed by hand)
15. Is not drinking well
16. Is losing weight
17. Is having diarrhea often
18. Is not urinating well
19. Is not moving normally
20. Is not as active as normal
21. Does not move around as needed
22. Needs my help to move around normally
23. Is unable to keep self clean after soiling
24. Has coat that is greasy, matted or rough-looking
25. How is my pet's overall health compared to the initial diagnosis/illness?
Once you have rated each prompt, tally up the number of responses for each number and then place an 'X' on a "Quality of Life line" labeled "Good" at one end and "Poor" at the other according to your most frequent response.
The purpose of this exercise is to help you better visualize your pet's general well-being. Of course, not all pets are the same and what is rated poorly for one may not be so bad for another. For pets currently undergoing treatment, some poor ratings may be liked to symptoms and side effects which will subside. It is always important to discuss your concerns and your pet's overall demeanor with your veterinarian, especially when considering humane euthanasia.
Domestic cats are descendants of the African wildcat, and many of the characteristic behaviors of these ancestors are still exhibited by cats today. An understanding of the origin and purpose of such behaviors can help cat owners appreciate their feline companions more fully and lead to an enhanced human-animal relationship.

Social Behavior
Once thought to be a social animals, it is now recognized that domestic cats can form complex social groupings. Studies have repeatedly shown that they form territories or ranges in which they live and defend these from intruders. In stable situations, cat territories can overlap without overt antagonistic interactions.
Communication
The cat has three primary methods of communication: vocal, visual and olfactory. Vocal communication involves a variety of sounds that convey different messages. Visual communication involves the body posture and facial expressions. For example, the position of the ears, hair and tail can offer important information about the emotional state of the cat. Olfactory communication plays a very important role in communication. The deposition of scents via facial marking, anal secretions and urine marking is an important communication tool for the feline.
Sexual Behavior
Female cats are seasonally polyestrus, with peaks in the Northern Hemisphere occurring from January to March and again from May to June. If they are not bred, estrus will last about 10 days and the female will cycle every three weeks for several months. During estrus, the female will engage in increased activity, vocalizations and marking with urine and other glandular secretions. Crouching with rear end elevated and rolling are common body postures that a female may exhibit during estrus.
Eating Behavior
In the wild, the cat developed as a solitary hunter that targeted various small prey. This led to an eating pattern of multiple small meals with considerable variety in the diet. Many domesticated cats continue this pattern and exhibit a preference for a variety of foods.
Bathroom Behavior
Kittens start to eliminate independently at about 4 weeks of age. They instinctively prefer to eliminate in fine particulate material with good drainage. Most cats will investigate a potential spot, dig a hole and pass urine or feces in the squatting position. Cats usually will then cover the elimination.
Sleeping Patterns
Although cats have traditionally been described as nocturnal creatures, they are actually crepuscular by nature, which means that they are more active in the twilight and evening hours. The average adult cat spends 10 hours per day sleeping and an additional five hours resting.
Ultrasound is a non-invasive, modern technique that produces a visual imprint of the interior of the body. It allows the doctor to achieve a depth of detail that is not possible with X-rays.
Echocardiography is a standard, non-invasive technique for assessing cardiac anatomy, pathology and function. High-frequency sound waves produced from a hand-held device are directed at the heart. The sound waves are reflected back to the machine and an image is produced. This image is transmitted to a video monitor where it can be seen. The image may be still or moving.
Veterinary Ultrasound Machine
Ultrasound uses sound waves, is non-invasive, painless, uses no dies and has no obvious harmful effects. It is perfect for diagnosing many types of heart problems.
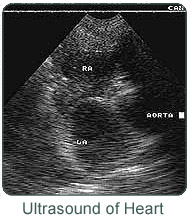
The heart is a very complex organ. It has four valves, an electrical conduction system, and four chambers, all of which are crucial to its function. As in people, animals suffer from a wide variety of heart diseases. In order to correctly diagnose and treat these diseases, it is necessary to see inside the heart, visualize the movement of the chambers, and to look at the valves in motion. This is the area where ultrasound predominates. Using ultrasound, it is possible to watch the heart in motion and to measure each of its’ parts. Ultrasound also allows the doctor or technician to measure the actual physical effects of various heart medications and to carefully adjust dosages.
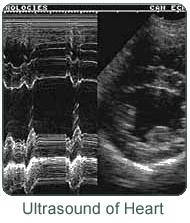
Most heart diseases are treatable, and in most cases, animals can live normal lives once the nature of their condition is under control.
Maintaining your dog in top physical shape and optimum health is the goal of every responsible dog owner. It is also your veterinarian's goal, and together, you can ensure that your pet stays healthy for years to come. Crucial to maintaining your dog's good health is the routine physical examination that your veterinarian performs on your pet.
Check-ups are important because they provide an opportunity to prevent diseases or even avoid them altogether. Unfortunately, many pet owners tend to underestimate the value of these visits because their pets appear to be healthy. However, this may be deceiving, since many diseases are often not evident in the early stages.
What Happens During A Wellness Examination?
Before the physical examination begins, your veterinarian asks you questions concerning your dog's state of health. This is very important for determining whether or not there are problem areas that need to be addressed. After obtaining a history, your veterinarian performs a physical examination on your dog. Starting at the head, your veterinarian examines the eyes, ears, face, and mouth. Examining the teeth is especially important since up to 85% of all dogs and cats over four years of age have some degree of periodontal disease! Early detection of periodontal disease is important, not only for effective treatment but also future prevention.

Health & Behavioral Risks to Consider
• Heartworm- Heartworm disease is a serious threat that causes cardiovascular weakness and lung incapacity. Caused by Dirofilaria immitis, these worms plug up blood vessels, which places an increased workload on the heart, along with restricted blood flow to the lungs, kidneys, and liver. This can eventually lead to multiple organ failure, including heart failure and death. Visible signs of the disease often do not appear before the infection has caused significant and irreversible internal damage. As part of an annual physical examination, your veterinarian can perform a simple test to detect heartworm disease and prescribe an easy-to-use preventive.
• Obesity- Your veterinarian can also determine whether or not your dog has an obesity problem. Obesity affects almost one out of every three pets, making it the most common nutritional disease among dogs and cats. Through visual assessment and palpation, your veterinarian can advise on whether or not your dog could benefit from a weight-reduction program.
• Diet- Diet is one of the most important considerations in health maintenance. Its importance lies not only in optimizing a pet's health, but also in the prevention and management of many diseases. Nutritional counseling is an essential part of the veterinarian's checkup and many owners use the opportunity to gain valuable advice on what to feed their pets.
• Obedience- Training is important for your pet's health because behavioral problems account for more deaths in dogs than any known disease. In fact, a well-trained and obedient dog is more likely to live to a ripe old age than a poorly trained one. Obedience-trained dogs are less likely to be involved in car accidents and dogfights, tend to be happier, and are less likely to have behavioral problems. The checkup provides an opportunity to discuss training techniques and behavior concerns with your veterinarian.
So you have a cute furry companion who loves to play fetch and go to the dog park. But are they well-behaved? It really doesn't matter whether your canine is a four-pound Chihuahua or a 104-pound Rottweiler. An untrained dog is an invitation to disaster. And a dog that won't come when called is always in danger.
As a pet owner, you should be committed to training your dog. So if your adorable companion has the tendency to bark to get your attention or to run away when you call for them, it's time to do something about ending that poor behavior.
Now for the good news: dogs are easily trained. That's probably the reason why dogs have long been America's favorite pet. Despite the fact that they train relatively easily, however, you still have to do the job. One way to make training simple is to get a breed that readily adapts to your lifestyle and that corresponds to what you want in a canine companion. Serious breeders can help you with this decision. They should tell you about their breed's inherent trainability—advice you should heed before making your final decision.

Rest assured that training does not strip a dog of natural instincts or "joie de vivre." After all, these are the things that attract people to dogs in the first place. We want you to celebrate the canine spirit, not abuse it.
What training does, however, is structure the dog's responses, giving you a good companion. Training gives you an animal you can trust, rely on, even flaunt. In fact, it establishes a channel of communication between you and your dog that significantly enhances your mutual respect and friendship.
Every civilized dog should know at least five basic commands: heel, sit, down, stay and come. These commands form the core of the exercises required for a Companion Dog degree in an American Kennel Club Novice Obedience competition. Even if you don't take your dog beyond these beginning lessons, they are absolutely essential in making every dog a true companion.
Incidentally, you train your dog to understand its name in much the same way you train it to do anything—by simple, repetitive action. As far as the name goes, make sure everyone in the household is using the same name. And, you can teach an older dog a new name, if you must.